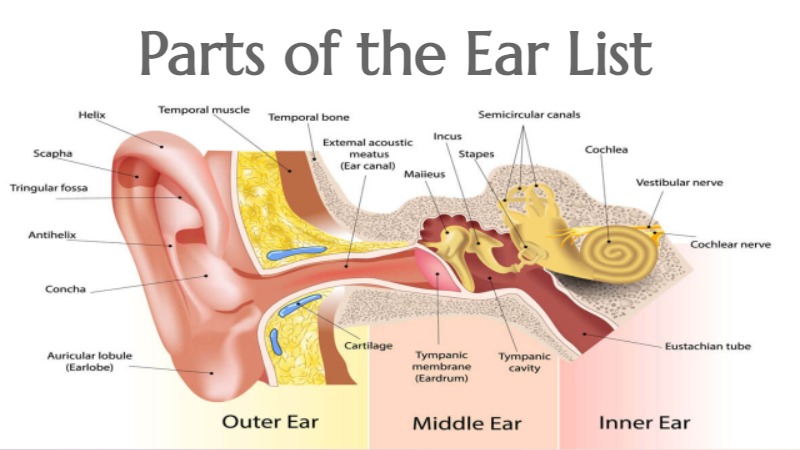
Parts of the Ear list with structural details of outer, middle and inner ear available, check functions of ear in a human body. The ear is a complex sensory organ responsible for hearing and maintaining balance. The outer ear collects sound waves, the middle ear amplifies and transmits the vibrations, and the inner ear converts these vibrations into electrical signals for the brain to interpret as sound. Additionally, the inner ear’s vestibular system helps with balance and spatial orientation.
The ear is a sensitive organ of the human body which is mainly concerned with detecting, transmitting and transducing sound. Maintaining a sense of balance is another important function performed by the human ear. Let us have an overview of the structure and functions of the 3 parts of the human ear. Also check problems associated with the ear and its symptoms.
Parts of the Ear
As we have told you that an ear in a human body consists of three main parts. Each part of the ear performs specific functions that contribute to our ability to hear and perceive sound.
- Outer ear
- Middle ear
- Inner ear
Let’s now describe each one of the following parts of the ear in detail.
Outer Ear
The outer / external ear is further divided into the following parts:-
- Pinna or Auricle: The visible part of the ear that helps collect and funnel sound waves into the ear canal. The auricle comprises a thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by a layer of skin. It consists of funnel-like curves that collect sound waves and transmits them to the middle ear. The lobule consists of adipose and fibrous tissues supplied with blood capillaries.
- Ear Canal: It channels sound waves towards the middle ear. The shape and length of the canal enhance specific frequencies and amplify sound.
Middle Ear
The middle ear comprises the following parts:-
- Eardrum (Tympanic Membrane): It separates the outer ear from the middle ear and vibrates in response to sound waves.
- Ossicles: These are the three tiny bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) that amplify and transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. There are three ear ossicles in the human ear.
- Malleus: A hammer-shaped part that is attached to the tympanic membrane through the handle and incus through the head. It is the largest ear ossicle.
- Incus: An anvil-shaped ear ossicle connected with the stapes.
- Stapes: It is the smallest ossicle and also the smallest bone in the human body.
- Eustachian Tube: It connects the middle ear to the back of the throat and helps equalize pressure between the middle ear and the environment.
Inner Ear
- Cochlea: The cochlea is a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled structure responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain.
- Vestibular System: Located in the inner ear, this system comprises the vestibule and semicircular canals, which are essential for maintaining balance and detecting changes in head position and movement.
- Auditory Nerve: This nerve carries electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain, allowing us to perceive and interpret sounds.
Function of Ear in Human Body
- Sound waves pass through the auditory canal and reach the eardrum.
- Vibrations produced pass through the tympanic membrane to the tympanic cavity.
- Ear ossicles in the tympanic cavity receive the vibrations and the stapes pushes the oval window in and out.
- This action is passed on to the organ of corti, the receptor of hearing, that contains tiny hair cells that translate the vibrations into an
- electrical impulse that are transmitted to the brain by sensory nerves.
- Eustachian tube and the vestibular complex are the important parts of the ear responsible for the balance.
- The eustachian tube equalizes the air pressure in the middle ear and maintains the balance.
- The vestibular complex contains receptors that maintain body balance.
Symptoms of Common Ear Conditions
There are a number of symptoms that could indicate a problem with your ears. These warning signs include:
- Ear pain
- Ear infection
- Clogged ears
- Muffled hearing
- Itchy ears
- Nausea and vomiting
- A feeling of fullness in your ears
- Ear drainage
Ear Problems List
There are many diseases and conditions that can affect your ears, check ear problems list here:-
- Ear infection (otitis media)
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Swimmer’s ear (otitis externa)
- Ruptured eardrum
- Otosclerosis
- Perichondritis
- Vestibular neuritis
- Meniere’s disease
- Ear injury
- Ear tumors
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist if you experience any persistent or concerning ear problems. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.